Chemistry is a branch of physical science that deals with the composition, structure, properties, and changes of matter. It involves the study of atoms, molecules, ions, and chemical reactions. Whether you’re a student exploring the subject or a professional chemist, understanding the foundational concepts is crucial. Here’s a cheat sheet that encompasses essential information about chemistry.
Atomic Structure
Atoms are the basic units of matter. They consist of three types of subatomic particles- protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are positively charged particles; neutrons are neutral particles, while electrons are negatively charged particles. The nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons, while the electrons orbit around the nucleus. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the atomic number of an element, which indicates its position in the periodic table. Elements can be classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids based on their properties.
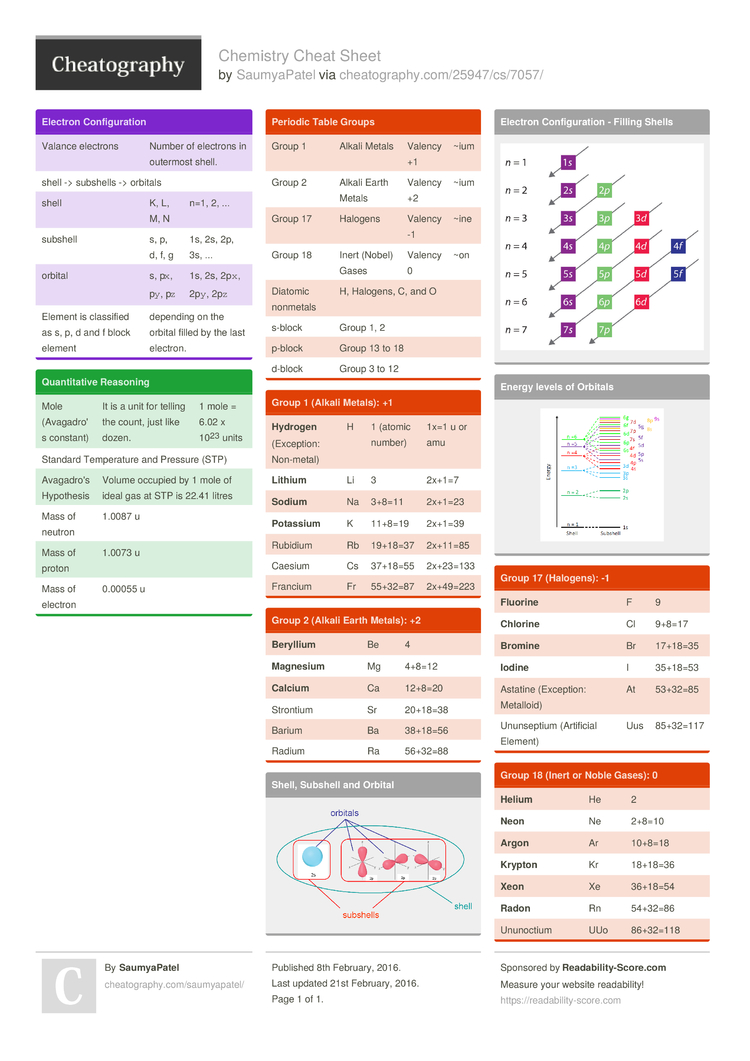 The electrons that orbit an atom are arranged in shells or energy levels. The first shell closest to the nucleus can hold a maximum of two electrons, while the succeeding shells can hold up to eight electrons. The electron configuration of an atom determines its chemical properties and how it reacts with other atoms to form compounds. There are two types of bonding- ionic and covalent. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
The electrons that orbit an atom are arranged in shells or energy levels. The first shell closest to the nucleus can hold a maximum of two electrons, while the succeeding shells can hold up to eight electrons. The electron configuration of an atom determines its chemical properties and how it reacts with other atoms to form compounds. There are two types of bonding- ionic and covalent. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions involve a rearrangement of atoms to form new substances. The reactants are the substances that undergo the reaction, and the products are the substances that are formed. Chemical reactions can be classified into various types- synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, combustion, and acid-base.
 The law of conservation of mass states that mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Therefore, the mass of the reactants must be equal to the mass of the products. Chemists use stoichiometry to calculate the quantities of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. The limiting reagent is the reactant that is completely consumed in the reaction and limits the amount of product formed. The theoretical yield is the maximum amount of product that can be obtained from a reaction, while the actual yield is the amount of product obtained in a laboratory.
The law of conservation of mass states that mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Therefore, the mass of the reactants must be equal to the mass of the products. Chemists use stoichiometry to calculate the quantities of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. The limiting reagent is the reactant that is completely consumed in the reaction and limits the amount of product formed. The theoretical yield is the maximum amount of product that can be obtained from a reaction, while the actual yield is the amount of product obtained in a laboratory.
Acids and Bases
Acids are substances that donate hydrogen ions in aqueous solutions, while bases are substances that accept hydrogen ions in aqueous solutions. Acids have a pH less than 7, while bases have a pH greater than 7. The pH scale is a logarithmic scale that measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. The stronger the acid, the lower the pH, while the stronger the base, the higher the pH.
 Neutralization is a chemical reaction between an acid and a base that results in the formation of water and a salt. The strength of an acid or a base can be determined using titration, a laboratory technique that involves the controlled addition of a standard solution to a sample solution until the reaction is complete. The equivalence point is the point at which stoichiometrically equivalent amounts of acid and base have been added, while the endpoint is the point at which the indicator changes color.
Neutralization is a chemical reaction between an acid and a base that results in the formation of water and a salt. The strength of an acid or a base can be determined using titration, a laboratory technique that involves the controlled addition of a standard solution to a sample solution until the reaction is complete. The equivalence point is the point at which stoichiometrically equivalent amounts of acid and base have been added, while the endpoint is the point at which the indicator changes color.
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its interconversion from one form to another. The first law of thermodynamics, also known as the law of conservation of energy, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. The second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a system, or the degree of disorder, tends to increase over time.
 The enthalpy change is the heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction at constant pressure. The entropy change is the measure of the degree of disorder in a system, while the Gibbs free energy change determines whether a reaction is spontaneous or nonspontaneous. A spontaneous reaction has a negative Gibbs free energy change and occurs without the input of external energy.
The enthalpy change is the heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction at constant pressure. The entropy change is the measure of the degree of disorder in a system, while the Gibbs free energy change determines whether a reaction is spontaneous or nonspontaneous. A spontaneous reaction has a negative Gibbs free energy change and occurs without the input of external energy.
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is the study of carbon-containing compounds and their reactions. Carbon has four valence electrons that allow it to bond with other atoms to form complex molecules. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms. Alkanes are hydrocarbons that have only single bonds, while alkenes and alkynes are hydrocarbons that have double and triple bonds, respectively.
 Functional groups are specific groups of atoms that determine the chemical and physical properties of organic compounds. Examples of functional groups include alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and amines. Organic reactions involve the breaking and formation of covalent bonds, and they can be classified as addition, substitution, elimination, or rearrangement reactions.
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms that determine the chemical and physical properties of organic compounds. Examples of functional groups include alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and amines. Organic reactions involve the breaking and formation of covalent bonds, and they can be classified as addition, substitution, elimination, or rearrangement reactions.
In conclusion, understanding the fundamentals of chemistry is essential for success in the subject. Hopefully, this cheat sheet has provided you with a quick reference guide to the key concepts in chemistry.